Electrical stimulation, or e-stim, is a physical therapy procedure that uses mild electrical pulses to stimulate sore or injured muscles, reduce inflammation, and relieve pain. In addition to speeding recovery, the procedure can be an effective alternative therapy for muscle pain that doesn’t respond to traditional treatments.
If you’re recovering from an injury or looking for relief from muscle pain—or if you want to preserve muscle mass or restore tone—e-stim therapy may be right for you.
What is EMS therapy?
Electrical muscle stimulation (EMS) is one of the main types of e-stim therapy. Other types include neuromuscular electrical stimulation (NMES) and transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), which targets nerves rather than muscles.
EMS therapy uses mild electrical pulses to reduce inflammation, ease muscle spasms, and relieve pain. Aiming continuous electrical bursts at particular muscles forces them to contract (or flex) and relax many times in a row.
During muscle stimulation, the body sends blood and oxygen to these areas and increases the production of endorphins, a natural pain reliever. The therapy helps decrease swelling, promotes muscle tone, and speeds the healing process. EMS therapy can also help strengthen and repair tissue that has weakened or atrophied due to injury or disease.
What to expect during an EMS therapy session
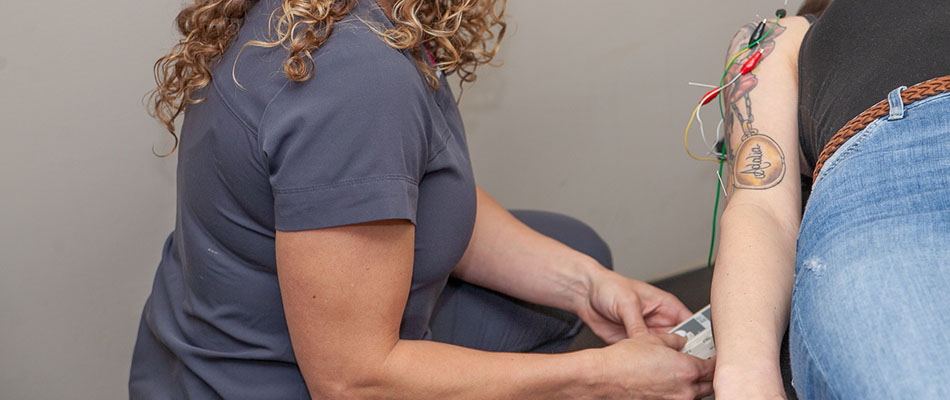
EMS therapy involves placing several electrodes on the skin near the affected muscles or source of pain. Each electrode is a small, sticky pad connected by a wire to an electrotherapy device that delivers a steady stream of electrical pulses to the electrodes.
The therapist begins on a low setting and gradually increases the electrical current during the session. Depending on the type of treatment, your muscles may contract or twitch repeatedly, and you may get a tingling sensation at the site. Most patients experience these sensations only during the treatment, but some feel the effects for up to 30 minutes after the session.
Sessions typically last from five to 20 minutes. Depending on your condition and the severity of your symptoms, you may need multiple sessions.
The benefits of EMS therapy for athletes
Doctors and physical therapists have used EMS therapy to treat athletes for decades. It’s an ideal solution for both pre-workout warmups and post-workout recovery. Many athletes depend on the therapy to soothe sore muscles and achieve their performance goals. Athletes who experience cramps or spasms may also benefit from treatments.
Regular sessions can help endurance athletes keep muscles loose so they can continue training without injury.
EMS therapy offers a number of benefits for athletes:
- Oxygenate muscles
- Increase blood flow
- Relieve pain
- Remove toxins, including lactic acid
- Release endorphins
- Promote muscle relaxation
- Enhance range of motion
- Reduce muscle spasms
- Prevent muscle atrophy
- Restore muscle tone
- Preserve muscle mass
Other uses of EMS therapy
In addition to training muscles and supporting athletic recovery, health care professionals use EMS therapy to treat a number of conditions and ease unpleasant symptoms. EMS can relieve lower back pain, reduce pressure on the sciatic nerve, and retrain muscles after surgery or a stroke.
This form of therapy can also keep muscles active and prevent atrophy after a spinal cord injury or during long periods of immobility. Stimulating muscles causes them to contract and relax, much like normal physical activity.
Doctors use a related type of e-stim therapy called TENS to treat joint pain, arthritis, fibromyalgia, carpal tunnel syndrome, and other medical conditions.
Is EMS therapy safe?
When administered by a health care professional, EMS therapy is safe and painless and has very few side effects. The most common side effect is mild skin irritation where the electrodes are placed.
However, EMS therapy is not recommended for people with a heart condition or for those who have a pacemaker or implanted heart device. If you are pregnant, talk to your doctor before starting EMS therapy. In most cases, the therapy is not recommended for pregnant people.
Are home electronic muscle stimulator units safe and effective?
The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) regulates the sale of all electrical muscle stimulators in the United States. While many companies advertise over-the-counter electrical stimulation units that promise to tone, firm, and strengthen muscles, the FDA has received reports of shocks, burns, skin irritation, and pain associated with the use of some devices.
The FDA has cleared many EMS devices that chiropractors and physical therapists use to treat patients in medical settings. Most FDA-approved EMS devices are intended for use in physical therapy or rehabilitation under the direction of a health care professional.
Get started with EMS therapy
Dr. Andrea’s Chiropractor Care offers a wide range of soft tissue and alternative therapies to work on restoring each patient’s whole-body health. Whether you are recovering from an injury, looking for an effective way to condition muscles, or simply seeking relief from everyday aches and pains, contact Dr. Andrea today or call us at 918-364-2225 to learn more about the benefits of EMS therapy.